Myth 1. “I’m obese, so I definitely have sleep apnea”.
FICTION
According to the Mayo Clinic, obesity greatly increases your risk of developing sleep apnea by the extra fat that causes an obstruction to your breathing while sleeping. However, it is a common misconception that all obese people have sleep apnea. People of all size can develop it especially if they have an irregular neck of facial anatomy. This can include the size of the tonsils, jaw, and neck (Ohayon, 1997).
Myth 2. “I’ve had sleep apnea for years, I don’t need to wear CPAP”.
FICTION
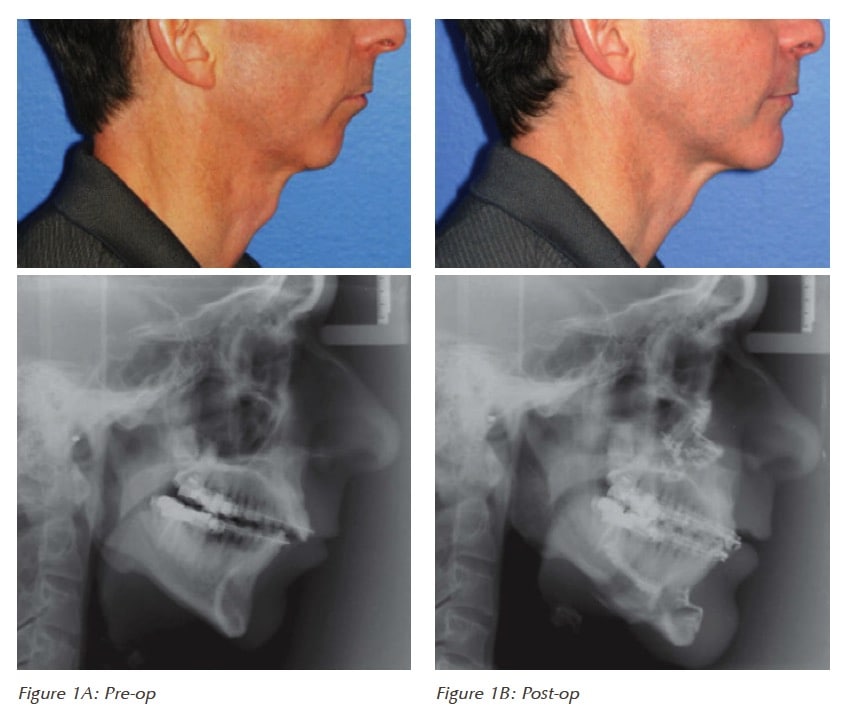
According to the American Association of Respiratory Care, CPAP is proven to be the most effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. But CPAP may not be the answer for everyone. Depending on your condition, you may seek other treatment like oral surgery or weight loss. Howver, if left untreated, you will be at greater risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, and more (Sandhya, 2020).
Myth 3. “I snore but I don’t have sleep apnea”.
FACT
Although snoring may be the number one sign of sleep apnea, it is not always the answer. Snoring can be caused by multiple factors like alcohol and nasal congestion. To truly know if you have sleep apnea, a sleep study must be performed. It’s a series of tests that will monitor your sleep patterns throughout the night.
References
Sandhya, P. (2020). Sleep apnea. Mayo Foundation for medical education and research. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20377631
Benjafield, A. (2019). Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnea: a literature-based analysis. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7007763/
Caples SM1, Rowley JA, Prinsell JR, Pallanch JF, Elamin MB, Katz SG, Harwick JD. Surgical modifications of the upper airway for obstructive sleep apnea in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. 2010 Oct;33(10):1396-407.
