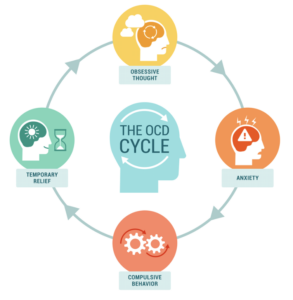
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a mental health condition characterized by persistent, intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions). Obsessions and compulsions reduce anxiety associated with these thoughts and can significantly interfere with daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Misconceptions
There are many misconceptions surrounding OCD that contribute to its stigmatization. It is important to recognize that OCD is a legitimate mental health disorder with biological, genetic, and environmental factors contributing to its development.
This parody video by Rhett and Link captures the misconception of OCD being the same as perfectionism. Some other misconceptions include:
| Assumption of Neatness and Organization: People with OCD are always neat and organized. | Reality: While some individuals with OCD may have a compulsion for cleanliness and order, OCD can manifest in various ways, including fears of contamination, intrusive thoughts, or repetitive checking rituals. |
| Personality Trait or Quirk: OCD is considered a personality trait or a personal quirk. | Reality: OCD is not a chosen behavior or personality trait. |
| Viewing Rituals as Superstitions: Rituals in OCD are seen as harmless superstitions. | Reality: Compulsive rituals in OCD are driven by intense anxiety and are not mere superstitions. They are attempts to manage overwhelming anxiety associated with obsessive thoughts. |
| Assuming Individuals Can “Just Stop” Their Behaviors: Individuals with OCD can easily stop their compulsive behaviors. | Reality: OCD is a complex mental health condition that often requires professional intervention. The urge to perform compulsions is driven by anxiety and stopping them can be challenging without appropriate treatment. |
| Overemphasis on Visible Symptoms: Only observable behaviors are indicative of OCD. | Reality: The internal distress caused by obsessive thoughts is a significant aspect of OCD. While compulsive behaviors may be visible, the obsessions are equally important and often hidden. |
Treatments
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT, specifically exposure and response prevention (ERP), is considered the gold standard for treating OCD. It involves gradually facing fears and resisting the urge to engage in compulsive behaviors.
- Medication: In some cases, medication, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms. It’s important to consult with a mental health professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
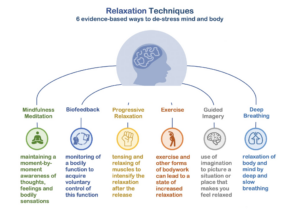
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as mindfulness meditation and deep breathing can help individuals stay grounded and reduce anxiety.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have OCD can provide a sense of community and understanding. Support groups or online forums offer a platform for sharing experiences and coping strategies.
Living with OCD
It’s crucial for individuals with OCD to tailor coping strategies to their specific needs and seek professional help when necessary. A comprehensive approach, combining therapy, medication (when prescribed), and self-help strategies, can contribute to effective management of OCD symptoms. Here are some general coping strategies for dealing with OCD:
- Deep Breathing: Practice deep breathing exercises to help calm the nervous system and reduce anxiety.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Mindfulness techniques can help individuals stay present in the moment, minimizing the impact of obsessive thoughts.
- Self-Compassion: Cultivate self-compassion and understanding. Recognize that living with OCD does not define your worth or capabilities.
- Education and Advocacy: Educate yourself about OCD and advocate for mental health awareness. By sharing your story, you contribute to reducing stigma and fostering a more compassionate society.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Establish realistic goals and celebrate small victories. Acknowledge the progress made, no matter how incremental.
- Therapy and Counseling: Work with a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist, who specializes in OCD. They can provide guidance, support, and evidence-based interventions.
Conclusion
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a complex and challenging condition, but with the right understanding, effective treatment, and a supportive community, individuals with OCD can lead fulfilling lives. By promoting awareness, empathy, and a comprehensive approach to well-being, we can collectively work towards dismantling the stigma surrounding OCD and fostering a more compassionate world for everyone.
References
Callaghan, L. (2020). How to treat OCD. Healthcare Counselling & Psychotherapy Journal, 20(4), 20–21. https://search-ebscohost-com.ezproxy.neit.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=146849259&site=ehost-live
Grant, J. E. (2019). OCD: A Common Psychiatric Disorder With a Constellation of Solutions. Psychiatric Times, 36(11), 33–38. https://search-ebscohost-com.ezproxy.neit.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=139818256&site=ehost-live.
Grant, J. E., & Chamberlain, S. R. (2020). Exploring the Neurobiology of OCD. Psychiatric Times, 37(7), 32–34. https://search-ebscohost-com.ezproxy.neit.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=144461603&site=ehost-live.
Knopf, A. (2021). OCD can be treated with internet‐CBT. Brown University Child & Adolescent Psychopharmacology Update, 23(8), 8. https://doi-org.ezproxy.neit.edu/10.1002/cpu.30602
Negreiros, J., Best, J. R., Vallani, T., Belschner, L., Szymanski, J., & Stewart, S. E. (2023). Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) in the School: Parental Experiences Regarding Impacts and Disclosure. Journal of Child & Family Studies, 32(9), 2848–2857. https://doi-org.ezproxy.neit.edu/10.1007/s10826-022-02350-w






 (2020)
(2020) (2022)
(2022)