
Myths and Facts of Anxiety
Many people experience periods of fear and worry, but those who have generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) are in a constant state of fear. Being able to maneuver through life without the continuous feeling of dread is considered a paradise for a person who has anxiety. We are going to take a looking into the symptoms, treatments, myths and facts of anxiety.
You Are Not Alone
According to National Health Statistics Report approximately 6.8 million adults have anxiety, yet less than 50% of those people are receiving treatment. The questions then become, what is anxiety, why do so many have it and how can it be treated.
SYMPTOMS
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), some of the signs that a person has anxiety are:
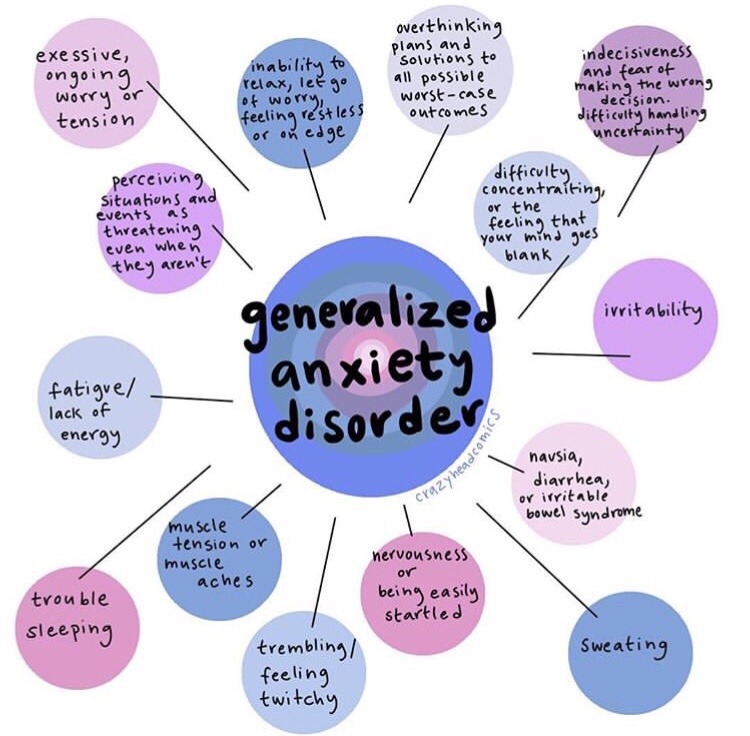 Feeling restless, wound-up or on the edge.
Feeling restless, wound-up or on the edge.
Having difficulty concentrating.
Being irritable.
Having unexplained pains i.e. muscle aches or frequent headaches.
Difficulty controlling feelings of worry.
Can’t fall or staying asleep.
Myths vs. Facts
There is a lot of misinformation about mental health disorders. As a result many people go untreated because they may believe that the myths are true and they are afraid of what other people may think. We’re going to take a close look at the myths and facts about anxiety disorder and what we can do to stay calm, cool, and collected.
Myth # 1
Is Anxiety Real?
One of the major misconceptions about anxiety is that it is not a true health condition.
Fact #1
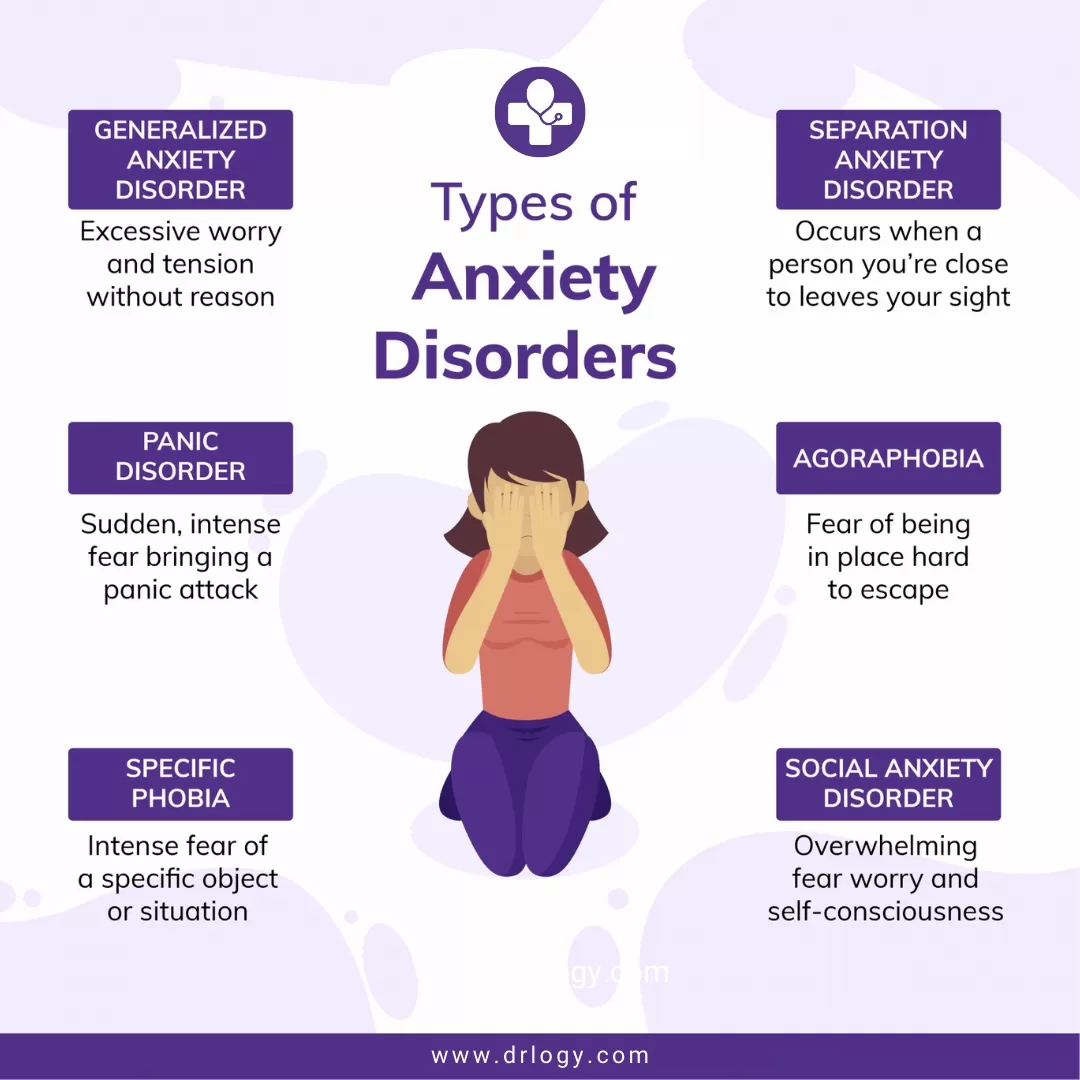
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) the most common form of anxiety is Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). Men, women and children can have anxiety but it is more common in women. People who have GAD tend to have extreme worry although there may not be reason to worry. The National Institute of Mental Health also state that the cause of GAD can be hereditary and some parts of the brain play key role in the anxiety.There are several different types of anxiety. In a study done by Mah et al., (2016) it is said that people who have anxiety disorders have their wires a little crossed in their brain resulting in exaggerated responses to perceived threats.
Myth #2
Are you able to take care of yourself?
A significant myth for those who suffer with anxiety is that they are unable to obtain/maintain employment and be productive members of society due to their disorder.
Fact #2
According to a study conducted by Redekkopp and Huston, a person who has a mental disorder such as anxiety it is important to their health and wellbeing to maintain employment. The experts believe that the environment the person is in plays a vital part in there ability to be successful at work. Having a positive work environment and flexible schedule can improve a persons mental health thus allowing them to be productive members of society.
Myth #3
All you need to do is a little yoga.
Many believe that man made medications do not help treat anxiety and the only type of treatment required is just yoga.
Fact#3
According to a study conducted by Lemay et al., yoga, meditation, and prescribed medications are treatments that can help a person who is experiencing symptoms of anxiety. The results of the study showed that people who participated in yoga and meditation session a minimum three times weekly had reduce periods of heightened periods of anxiety (Lemay et al., 2019). Additionally, a study conducted by Bledsoe & Baskin suggest that along with yoga and meditation, prayer, self talk and maintaining a mental checklist where positive skills that will help with managing periods of anxiety. Examples of how the mental checklist can be implemented can be found in a book titled Taking control of anxiety: small steps for getting the best of worry ,stress and fear. In this book one of the mental checklist tools use was the what if method also known as the if…. then… method. The what if method consist of writing down your fear followed by a series of questions (Moore, 2014). This tool allows you to use self awareness and realize that the fear my be blown out of proportion.
Treatments for Anxiety
Therapy
Meditation, yoga and checklist many not work for everyone who has anxiety. Medications and therapy can also help with managing the disorder. There are several different types of therapy that have proven to be very affective in treating anxiety. One type of therapy is acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT). The benefit of ACT is that it teaches skills on how to use tasks that are important to you in order to function in your daily life (Lawrence et al.,2019). According to the national institute of mental health another effective type of therapy is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). This type of therapy teaches you how to view things in a different way in order to manage your symptoms better. CBT is also used together with exposure therapy which requires you to confront the underlying cause of the anxiety disorder.
Medications
In the event therapy and yoga don’t improve your symptoms there are medications that can help. The medications typically prescribed for a person who is having severe symptoms of anxiety are antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications such as sedatives and herbal medicines. Taking this medications must be under the guidance of a licensed physician to ensure proper dosage and reduces the chances of misuse.
Support Groups
For some people who feel that medications and therapy just aren’t working joining a support group may be the way to go. This will allow you to you to share your problems and successes with others who are having the same difficulties. If your looking to join a support group contact the Peer Support Line at 844-444-0152.
Conclusion
Information about healthcare is forever changing as a result misinformation will continue to be present. Having reliable resources to fact check a myths is vital for some who is anxious and needs to know the reason for everything that is happening in their daily lives. Without reliable resources to debunk medical myths people will continue to have symptoms that may go untreated. It is essential to remember when you have a doubt about any medical misinformation use reliable resources to determine whether it is a myth or fact.
References
Bledsoe, S., Baskin, J. J., & Berry, F. (2018). Fear not! How students cope with the fears and anxieties of college life. College Teaching, 66(3), 158-165. https://doi.org/10.1080/87567555.2018.1472064
Lawerence, V., Kimona, K., Howard, R. J., Serfaty, M. A., Wetherell, J. L., Livingston, G., Wilkinson, P., Walters, K., Jones, R., Wuthrich, V. M., & Gould, R. L. (2019). Optimising the acceptability and feasibility of acceptance and commitment therapy for treatment-resistant generalised anxiety disorder in older adults. Age and Ageing, 48(5), 741-750. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afz082
Lemay, V., Hoolahan, J., & Buchanam, A. (2019, June 8). Impact of a Yoga and Meditation Intervention on Students’ Stress and Anxiety Levels. PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31333265/
Mah, L., Szabuniewicz, C., & Fiocco, A. J. (2016). Can anxiety damage the brain. Current opinion in psychiatry, 29(1), 56-63. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000223
Moore, B. A. (2014). Taking control of anxiety: Small steps for getting the best of worry, stress, and fear. American Psychological Association.
National Institute if Mental Health. (n.d.). Anxiety disorders. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). (n.d.). Generalized anxiety disorder: When worry gets out of control. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/generalized-anxiety-disorder-gad
Redekopp, D. E., & Huston, M. (2019). The broader aim of career development:Mental health, wellbeing and work. British Journal of Guidance & Counseling, 47(2), 246-257. https://ezproxy.neit.edu/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx? direct=true&db=eric&AN=EJ1216522&site=ehost-live
Zablotsky, B., Weeks, J., Terlizzi, E., Madans, J., & Blumberg, S. (2022, July 11). NationalHealth Statistics Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhsr/nhsr172.pdf
